The Unintended Consequences of Cancer Therapies on Brain and Eye Protection
Recent research from the University of Minnesota has unraveled a surprising connection between a well-known cancer pathway and the protective barriers of our brain and eyes. This breakthrough study has revealed that increasing levels of the tumor-suppressing protein p53 may weaken the blood-brain and blood-retina barriers by interfering with Norrin/Frizzled4 signaling. In this editorial, we will take a closer look at these findings, explore the potential implications for current cancer therapies, and discuss why this research is crucial for our understanding of vascular health in the central nervous system.
These findings open up a realm of curiosity and caution, especially for those treatments aimed at boosting p53 levels to combat cancer. The study’s results indicate that while p53 is well-known for protecting against cancer, its augmented activity may come at a cost: impaired barrier function in critical parts of the body, which may lead to neuroinflammation and vascular dysfunction. We are now challenged with managing these conflicting outcomes—combating cancer on one front while protecting the subtle parts that preserve brain and eye health.
Understanding the p53 Pathway and Its Dual Role
The p53 protein is a crucial component in our natural defense against cancer. Under normal conditions, p53 helps curb the growth of abnormal cells, effectively putting a brake on tumor development. However, as this study shows, the augmented presence of p53 may also signal unintended consequences when it comes to the maintenance of blood–CNS barriers.
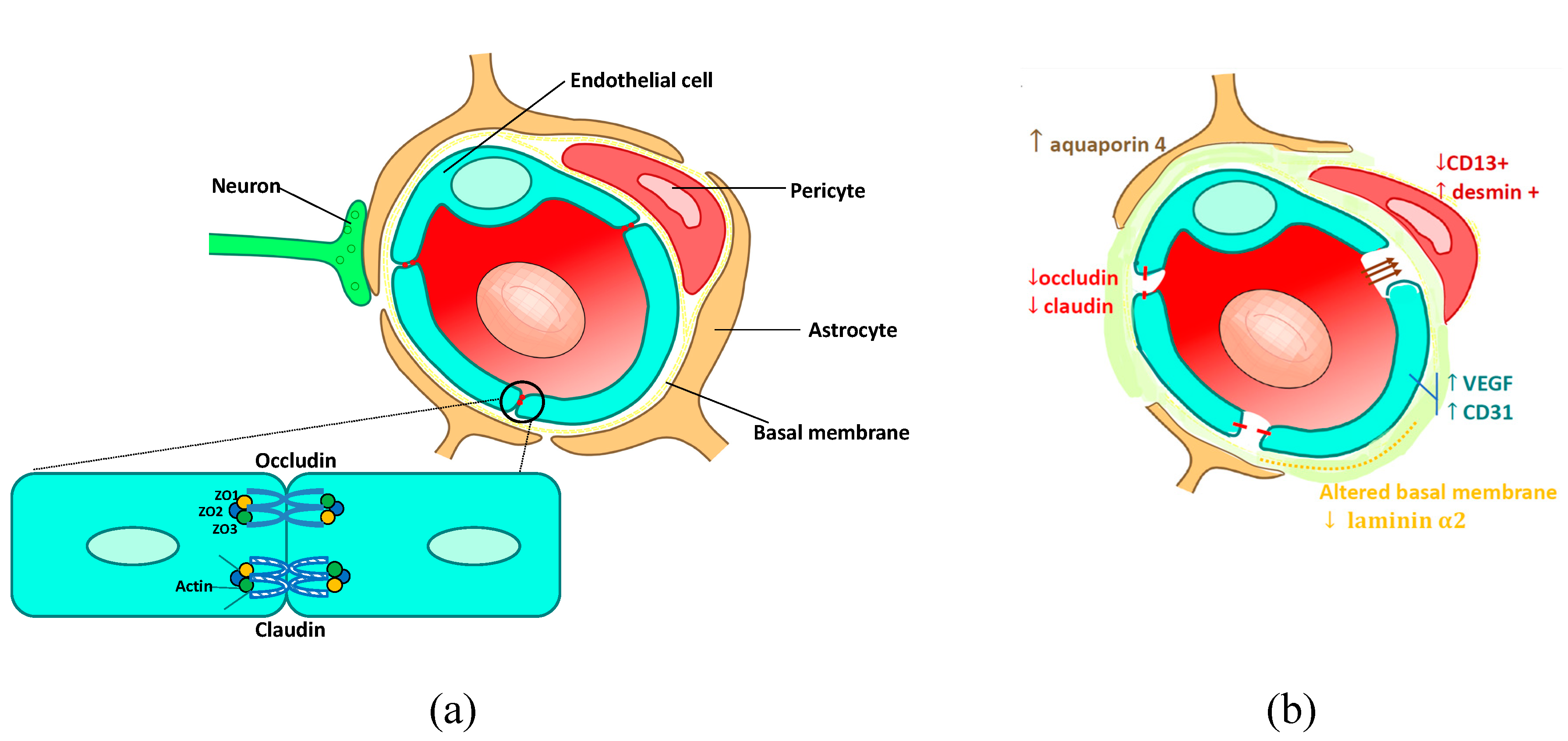
How p53 Affects Blood-Brain and Blood-Retina Barriers
Under normal circumstances, our blood–brain and blood–retina barriers serve as the body’s frontline defenders. They regulate the exchange of nutrients and hormones, while keeping harmful agents at a safe distance from our nerves and sensitive tissues. The study indicates that p53, when present in high quantities, interferes with the Norrin/Frizzled4 signaling pathway. This interference leads to reduced levels of NCAPH, a protein that has now been implicated as a potential player in inherited conditions such as familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR).
Key Points on Barrier Function and p53’s Role:
- Elevated p53 disrupts the fine points of Norrin/Frizzled4 signaling.
- This disruption causes a drop in NCAPH levels—integral for barrier stability.
- Weakened barriers can lead to unregulated transport between the blood and central nervous system.
- The impaired function may set the stage for neuroinflammation, swelling, and vascular dysfunction.
While these observations might seem like a tangled issue at first glance, they hold significant implications for how we approach cancer therapy. It becomes critical not only to treat the tumor but also to protect these delicate defenses that prevent further complications.
Examining the Impacts of MDM2 Inhibitors on Vascular Health
One of the promising approaches in cancer treatment involves the use of MDM2 inhibitors. These drugs are designed to boost the levels of p53 by blocking its negative regulator, MDM2. However, as the research highlights, increasing p53 might inadvertently lead to complications that affect the brain and eyes.
Potential Hazards of MDM2 Inhibitors
The MDM2 inhibitors are among the frontline therapeutic agents being developed to battle various cancers. Their primary role is to enhance p53’s tumor-suppressing abilities. But when the levels of p53 are raised too much, it may weaken the blood–CNS barrier’s strength. This unintended side effect is especially concerning in a vulnerable system already on edge.
Here is a summary of the risks posed by MDM2 inhibitors based on recent findings:
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased p53 Levels | Disruption of Norrin/Frizzled4 signaling |
| Reduced NCAPH Expression | Weakening of the blood-brain and blood-retina barriers |
| Barrier Dysfunction | Unregulated nutrient and molecular transportation; possible neuroinflammation |
| Vascular Health Concerns | Risk of retinal and brain swelling along with broader vascular issues |
This table provides a snapshot of the delicate balance that must be maintained. The challenge for researchers and physicians now is to find ways to harness the benefits of increased p53 while ensuring that the protective barriers remain intact. Patients undergoing such treatments could, in theory, face additional complications if these vascular functions are compromised, highlighting a need for further clinical investigation.
NCAPH: A New Candidate Gene in Eye and Vascular Disorders
Beyond the immediate concerns about p53 and related pathways, there’s an emerging spotlight on a gene called NCAPH. The study posits that NCAPH might be linked to conditions such as familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR), a rare inherited disease affecting retinal blood vessel development.
Significance of NCAPH in Vascular Health and Retinal Diseases
While the role of NCAPH in blood vessel formation is still being explored, early data suggests that this gene is essential for maintaining the structure and function of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells are the building blocks of blood vessels, making NCAPH a potential key player in both vascular disorders and inherited retinal diseases.
Below is a bulleted list of the possible roles NCAPH might play in vascular and ocular health:
- Regulator of endothelial cell proliferation and function
- Contributor to the overall integrity of blood vessel barriers in the central nervous system
- Potential factor in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy by affecting retinal angiogenesis
- A downstream effector of p53, linking cancer pathways directly to vascular health
Understanding the fine shades of NCAPH expression may offer a launching point for new therapeutic targets. Interventions aimed at modulating NCAPH could potentially restore barrier integrity in those suffering from vascular complications due to overactive p53 signaling. This line of research, though still in its early days, is one that warrants further exploration.
Balancing Cancer Therapy with Vascular Protection
There is no doubt that the fight against cancer is one of the most nerve-racking challenges in modern medicine. Yet the journey is full of tricky parts and tangled issues, as increasing evidence shows that every step forward in one area could inadvertently create problems in another. The current findings suggest that boosting p53 to combat cancer may create a double-edged sword, addressing one problem while potentially introducing new ones in brain and eye health.
Strategies to Reduce Unwanted Consequences
Physicians and researchers face the overwhelming task of finding a middle ground between effective cancer treatment and the preservation of holistic health—particularly the integrity of our brain and eye barriers. Some potential strategies include:
- Refined Dosing: Tailoring the dosage of MDM2 inhibitors could minimize the impact on barrier functions while still promoting cancer cell death.
- Combination Therapies: Using adjunct treatments that protect or restore barrier integrity could help counteract the negative side effects of elevated p53 levels.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Implementing rigorous monitoring protocols for vascular health during treatment, particularly for populations at risk for neuroinflammation and retinal complications.
- Gene-Specific Research: Further exploring the role of NCAPH may open doors to targeted therapies that address both cancer and vascular dysfunction simultaneously.
These strategies, while still in preliminary stages, represent a step towards finding your path in managing the latent challenges of modern cancer therapy. They underscore the importance of adopting a multifaceted treatment approach, one that not only attacks tumors but also protects the complex pieces that maintain systemic health.
Implications for Future Research and Clinical Practice
The revelations from this study have several layers of significance for both ongoing research and everyday clinical practice. As we come to grips with these subtle details, it is essential to rethink our approach to targeting cancer pathways, especially in a context that includes the fragile and essential blood–brain and blood–retina barriers.
Key Areas Requiring Further Investigation
Future research must address several pressing questions to bridge the gap between experimental findings and clinical application:
- How can therapies be optimized to maximize anti-tumor efficacy while minimizing barrier dysfunction?
- What additional protective measures can be implemented during treatment to safeguard against neuroinflammation and vascular issues?
- Can the role of NCAPH be further clarified to serve as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target for retinal and vascular diseases?
- What patient populations might be most at risk, and how can personalized medicine approaches help mitigate these risks?
Clinical trials must also adapt to these insights. They should include detailed vascular assessments and monitoring protocols to ensure that any treatment-induced damage to the brain or eye barriers is promptly identified and managed. Such comprehensive evaluations could lead to the development of combination therapies or protective adjuncts that secure barrier function even when p53 levels escalate.
Understanding the Broader Context: Cancer, Inflammation, and Vascular Health
When we put cancer treatments into perspective, it’s clear that medicine is working through a labyrinth of interconnected systems. Every treatment, while targeting a specific problem area, also interacts with various other systems in the body. The interplay between cancer, inflammation, and vascular health is rich in both promising avenues and potential pitfalls.
Complex Connections Between Tumor Suppression and Barrier Integrity
One of the most intriguing aspects of this study is the revelation that a protein, celebrated for its cancer-fighting properties, can also compromise the small distinctions that keep our brain and eye barriers intact. This connection is more than a mere side note—it is a reminder that the human body operates through a web of interdependent processes. Key considerations include:
- The delicate balance between tumor suppression and barrier maintenance
- The role of stress responses in influencing vascular permeability
- Potential downstream effects, such as neuroinflammation and edema, that follow barrier disruption
These points underscore the need for a holistic perspective when developing treatments. Future medicine will likely need to combine therapeutic strategies that address both cancer cell proliferation and the preservation of healthy vascular function.
Managing Your Way Through New Treatment Protocols
For both patients and physicians, the evolving landscape of cancer therapy necessitates a proactive stance when it comes to managing your way around new treatment protocols. On one level, the advancements in targeting the p53 pathway are promising, but on another, they require careful management to ensure that secondary complications like barrier dysfunction do not offset the primary benefits.
Steps for Physicians and Researchers
Here are some actionable steps that clinicians and researchers can consider as they work through the challenges posed by these findings:
- Patient Education: Ensure that patients are fully informed about both the potential benefits and the subtle risks associated with their treatments. Clear communication is key to helping patients figure a path through their treatment journey.
- Routine Imaging: Adopt routine imaging or vascular assessments as part of cancer therapy protocols, particularly when treatments known to elevate p53 levels are used.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between oncologists, neurologists, and ophthalmologists so that any signs of barrier dysfunction can be detected early and managed effectively.
- Preventive Measures: Explore techniques and medications that can help reinforce barrier integrity, potentially offsetting the unwanted effects of MDM2 inhibitors.
These steps illustrate that while the road ahead is full of confusing bits and nerve-racking challenges, concerted efforts in research and clinical practice can result in treatment strategies that safely balance cancer suppression with the preservation of essential body functions.
Looking Ahead: Integrating Novel Insights into Patient Care
It is super important that these insights transition from the laboratory to the patient’s bedside. As researchers continue to dig into the connections between cancer pathways and vascular integrity, we must not lose sight of the ultimate goal: improving patient outcomes. The current findings affirm that modern medicine still faces hidden complexities in systems otherwise considered well understood.
Potential Clinical Applications
Looking toward the future, the integration of these research discoveries into everyday clinical care could take several promising forms:
- Customized Therapeutic Regimens: With a clearer understanding of these molecular pathways, doctors can design treatment plans that account for a patient’s unique vascular health profile.
- Predictive Biomarkers: Both p53 and NCAPH could serve as predictive biomarkers to identify patients who are at greater risk of experiencing barrier dysfunction during treatment. This is essential when planning personalized therapies.
- Combination Strategies: Incorporating barrier-protective agents alongside conventional cancer treatments might help reinforce the blood–brain and blood–retina barriers, ensuring that crucial systems remain unharmed.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Post-treatment protocols can include monitoring for signs of neuroinflammation or retinal issues. Preventative strategies might be implemented to manage any late-arising complications.
These potential applications demonstrate that while the discovery of p53’s dual role is an off-putting twist, it also offers valuable avenues for holistic treatment approaches. Patients may eventually benefit from therapies that are attuned not only to killing tumors but also to safeguarding overall health.
Reflections on the Journey of Modern Medical Research
Modern medical research is on a constant quest to perfect treatment strategies. The journey of deciphering the roles of p53 and NCAPH in both cancer suppression and vascular integrity is a classic example of the twists and turns that define scientific progress. Every new discovery brings with it a set of challenging questions—questions that require us to get into the nitty-gritty of biological interactions and work through the potential pitfalls of targeted therapies.
The balance between pushing the boundaries of what is possible in cancer treatment and ensuring the safety of other delicate systems remains a key area of focus. As treatment modalities become ever more advanced, it’s critical that they also address the broader implications for overall patient well-being.
Lessons Learned and Future Directions
From this study, several lessons can be drawn that will be useful as we look ahead:
- The body’s interconnectivity: Even the most targeted therapy can have widespread effects. Recognizing this interdependence is vital in creating balanced treatment plans.
- The role of protective barriers: The blood–brain and blood–retina barriers are integral to human health. Their proper function must be preserved, even amidst aggressive cancer treatments.
- Personalization in healthcare: As we learn more about individual genetic components like NCAPH, personalized therapy that addresses both cancer and vascular health will become increasingly important.
- Interdisciplinary research: Collaborative efforts between oncology, neurology, ophthalmology, and pharmacology will be key in addressing the full spectrum of treatment effects.
These lessons highlight the importance of taking a comprehensive approach to modern medicine. The challenges may be overwhelming at times, but they also spur innovative thinking and encourage us to take a closer look at the subtle parts of our biological systems that make life possible.
Charting a Course Forward: Policy, Research, and Public Awareness
In light of these findings, it is essential that all stakeholders—from researchers to policymakers—work together to address the full array of challenges posed by novel cancer treatments. The unexpected effects of p53 augmentation on barrier integrity serve as a wake-up call that medical advancements must always be balanced with the protection of fundamental body functions.
Implications for Health Policy and Funding
For health policymakers and funding bodies, there are several considerations:
- Enhanced Funding for Multidisciplinary Research: Encouraging research that bridges oncology with neurology and ophthalmology is crucial. Collaborative projects can help unravel the tangled issues of barrier integrity while targeting cancer effectively.
- Policy Guidelines for Clinical Trials: New guidelines might be needed that mandate vascular health assessments as part of clinical trials for MDM2 inhibitors and other therapies that elevate p53.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the potential risks and benefits of emerging cancer therapies can empower patients to make informed decisions with their healthcare providers.
These steps will help ensure that the full impact of cancer therapies is understood and that resource allocation supports research not just into tumor biology but also into the preservation of systemic health.
Community Engagement and the Role of Advocacy
Patients, caregivers, and advocacy groups all have a role to play. By staying informed about breakthroughs and supporting comprehensive research initiatives, the community can help steer talk and action towards treatments that are both powerful and safe.
- Patient Advocacy: Engage with local and national organizations that advocate for comprehensive cancer care, ensuring that treatment strategies consider overall quality of life.
- Health Literacy Campaigns: Support educational efforts aimed at explaining how complex biological systems interact. This can help dispel myths and clarify that advances in one area of medicine might influence other aspects of health.
- Collaborative Networks: Patients and doctors alike can benefit from networks where emerging issues are openly discussed, shared, and addressed collectively.
These community-driven initiatives are super important as they bring the subtle details of recent scientific discoveries into broader public knowledge. In doing so, they help ensure that therapeutic advances are implemented safely and responsibly.
Conclusion: The Path Ahead in Integrating Cancer Therapies with Vascular Safety
The study from the University of Minnesota has cast light on how a critical protein like p53, celebrated for its role in warding off cancer, might also weaken the decidedly delicate pieces that form our blood–brain and blood–retina barriers. These discoveries are a clear reminder of the hidden complexities that lie in the fine balance between aggressive cancer treatments and the protection of other essential body systems.
As researchers continue to poke around and figure a path through these new challenges, it becomes increasingly clear that future treatment protocols must be designed with a dual focus: one that is determined to fight cancer while also preserving the intricate vascular networks that protect our most sensitive organs.
For clinicians, researchers, and policymakers, this journey is both exciting and intimidating. The findings challenge us to manage our way through the tricky parts of modern medicine by pairing effective tumor suppression with strategies that maintain barrier integrity. Such balanced approaches may include refined drug dosing, combination therapies, and persistent monitoring of vascular health, ensuring that both cancer and its unintended side effects are managed with care.
Ultimately, the emerging dialogue surrounding p53, NCAPH, and MDM2 inhibitors calls for an all-encompassing research approach—one that recognizes that our bodies are multifaceted and that our fight against disease must protect the very systems that keep us healthy in the first place. With thoughtful integration of scientific insights into clinical practice and health policy, we can pave the way for treatments that not only extend life but also enhance its quality.
In the end, the task is clear: we must continue to dig into these tangled issues, carefully balancing the need for effective cancer treatments with the essential requirement to protect the subtle, critical barriers that shield our brain and eyes. Only then can we truly claim to have mastered the twists and turns of modern medicine.
By embracing such comprehensive strategies, the medical community can ensure that progress in cancer therapy does not come at the cost of overall vascular health, thereby charting a course for a future where treatments are as safe as they are innovative.
As we move forward, let us take a closer look at every decision and every treatment strategy, mindful of the potential ripple effects they may have on every tricky part of our body’s intricate defense system, ensuring a balanced, informed, and patient-centered approach to modern healthcare.
Originally Post From https://neurosciencenews.com/cancer-pathway-retina-brain-29434/
Read more about this topic at
Cancer Pathway Found to Weaken Brain and Eye Barriers
P53 in lung vascular barrier dysfunction – PMC
